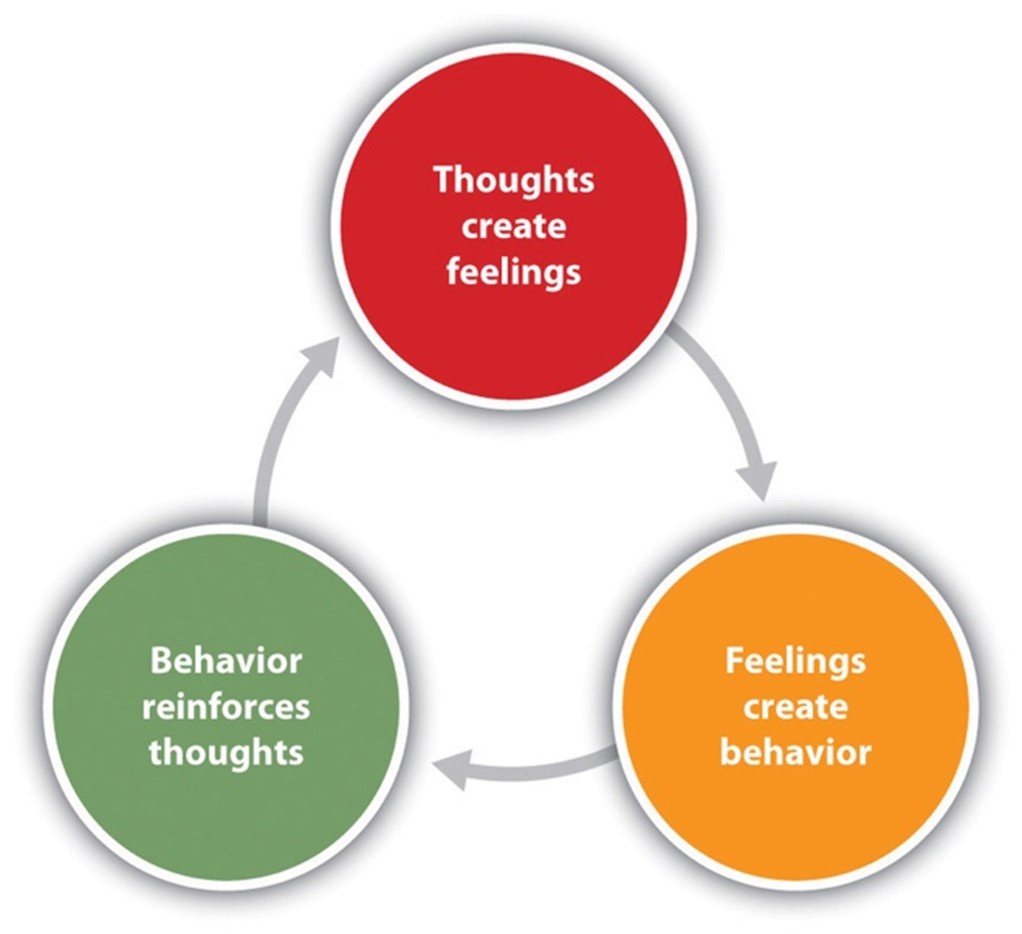
What is CBT?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, or CBT as it is often referred, is one of the most commonly used treatment modalities in the mental health field. Within the CBT approach, the understanding is that human concerns often arise due to faulty or unhelpful thought patterns or beliefs that people may hold about themselves or certain events that occur in their lives. Often times, those unhelpful thoughts lead to problematic emotions and behavioral results. A therapist practicing CBT will likely focus on the ways in which thoughts, emotions, and behaviors all interact with one another in each individuals’ life.
The goal of CBT is to address the interplay between thoughts/beliefs, emotions, and behavior in order to dispute or modify any unhelpful thoughts that may be negatively impacting clients’ wellbeing.
What are some CBT Techniques?
- Some techniques you might see used in CBT are:
- Unraveling cognitive distortions à in other words, identifying faulty thought patterns and then challenging those patterns to encourage new thoughts, feelings, and behaviors
- Cognitive restructuring à exploring potential causes of faulty thinking then looking to reframe and restructure those unhelpful thoughts
- Journaling à used to encourage self-reflection and identify various thought patterns, both helpful and unhelpful
- Progressive muscle relaxation à a technique used to mindfully focus on physical relaxation
- Interoceptive exposure à this is often used to treat panic attacks and anxiety by purposefully and gently exposing clients to their sensations of panic in a safe space in order for clients to gain an understanding that their sensations are not dangerous, which is shown to help with coping when anxiety or panic sets in
What mental health concerns is CBT commonly used to treat?
- CBT is used to treat a wide range of mental health concerns, such as:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Substance use
- Relational problems
- Eating disorders
- Severe mental illness